PCIe slots are expansion slots used to connect PCIe devices to a computer. PCIe is an abbreviation for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express and refers to the standard interface used by GPUs, sound cards, wifi cards, and other high-speed components.
Most modern motherboards use two interfaces for connecting components: PCIe and SATA. SATA is used for connecting slower devices such as hard drives and optical drives, while PCIe is used for connecting faster devices such as GPUs and NVMe SSDs.
But not all PCI express slots are the same. They have different sizes, speeds, and generations and can be used for various purposes. If you want to learn everything there is to know about PCIe slots, then keep reading!
What is PCIe?
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a standard interface used on motherboards for connecting GPUs, sound cards, wifi cards, and other high-speed components. It was first introduced in 2004 and has since been revised several times.
The latest revision is PCIe 5.0, which is only supported by the latest Z690 motherboards for Intel’s 12th generation processors. The previous revision, PCIe 4.0, is still the most commonly used version supported by most motherboards.
What are PCIe slots?
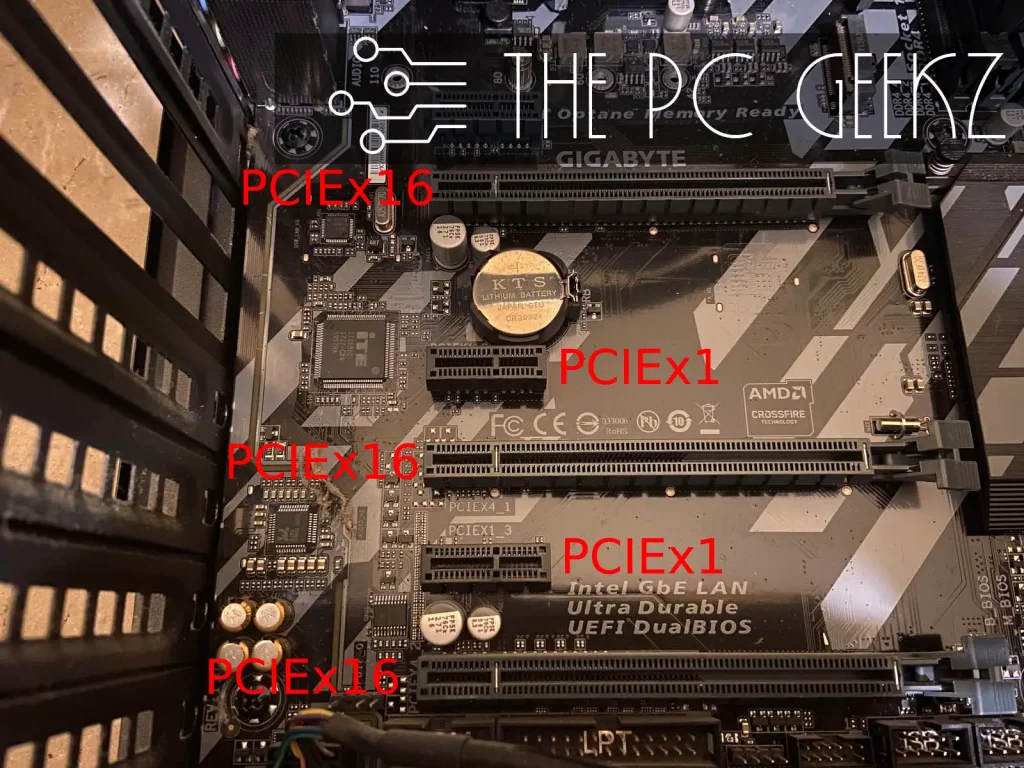
PCIe slots are slots on your motherboard that use the PCIe standard to connect PCIe devices to your computer. They have different sizes and speeds and are used for different expansion cards.
Different PCI Express Slot Sizes
As I already mentioned, PCI express slots have different sizes and speeds. The most common size is the x16, which is used for graphics cards. Other standard sizes are x1, x4, and x8.
They have different physical sizes, with the x1 being the smallest and the x16 being the largest.
But the physical size is not the only difference between these slots. They also have different data transfer speeds and a different number of lanes.
What Are PCIe Lanes?
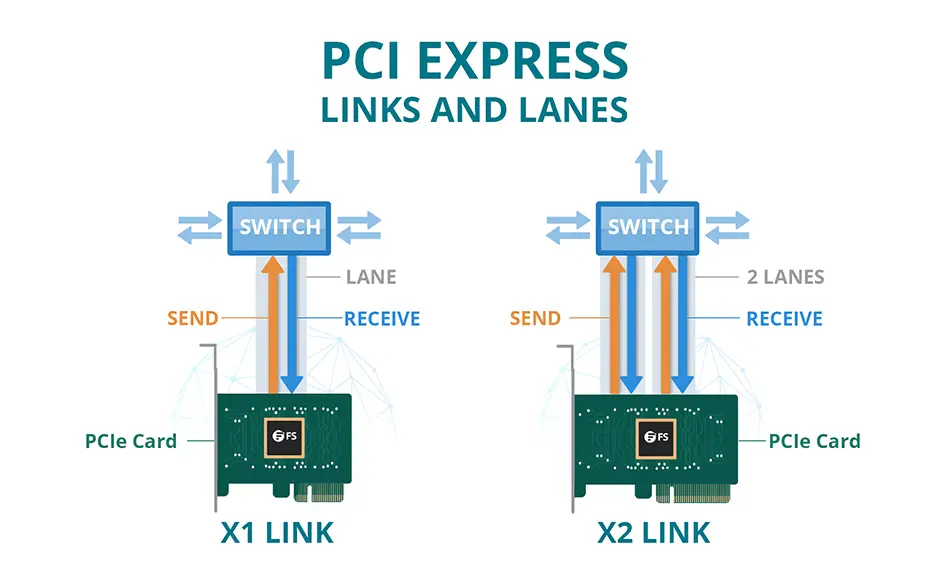
The PCIe lanes are the data highways that connect the PCIe devices to the computer and the more lanes a slot has, the faster it can transfer data.
Different PCI express slot sizes have different numbers of lanes. The x1 slot has one lane, the x4 slot has four lanes the x8 slot has eight lanes, and the x16 well could have anywhere between four to sixteen lanes (more on that later).
As you can understand, the number of PCIe lanes and the data transfer speed are directly related. The more lanes a PCIe slot has, the faster it can transfer data. Your motherboard’s chipset and CPU determine the number of lanes, and a standard computer will have 20 to 24 PCIe lanes across all slots. But keep in mind that not all lanes will be available for expansion slots; some could be used for other devices such as SATA controllers and USB headers.
Related Article: How Many PCIe Lanes Do I Have?
What Are PCIe Generations?
PCI Express lanes are not the only factor determining a PCIe slot’s data transfer speed. The other aspect is the PCIe generation.
The PCIe generation, aka PCIe gen, is simply the version of the PCIe standard a slot is using. The most recent generation is 5.0, introduced in 2021 with the release of Intel’s Z690 chipset.
The previous generation, 4.0, is the most commonly used one and is supported by most motherboards.
The table below shows the data transfer speeds of each PCIe generation at different lane counts. As you can see, combining a higher lane count and a newer generation results in much faster data transfer speeds.
| Generation | x16 GB/s | x8 GB/s | x4 GB/s | x2 GB/s | x1 GB/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 | 63.015 | 31.508 | 15.754 | 7.877 | 3.938 |
| 4.0 | 31.508 | 15.754 | 7.877 | 3.938 | 1.969 |
| 3.0 | 15.754 | 7.877 | 3.938 | 1.969 | 0.985 |
| 2.0 | 8.000 | 4.000 | 2.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 |
| 1.0 | 4.000 | 2.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 0.250 |
Related Article: Which PCIe Slot For GPU Is The Best?
What do PCIe slots look like?
I know that after all the technicalities, some of you might be wondering what PCIe slots look like. So, I have attached a few pictures showing different types of PCI express slots below.


PCIe slot sizes and their uses
Now that you know about the different sizes, speeds, and generations of PCI Express slots, you might be wondering what each one is used for.
The PCIe x16 Slot
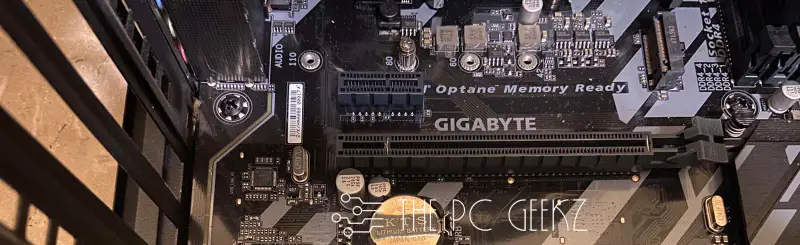
The most popular and standard slot size is PCIe x16. It is almost always used for graphics cards, as they need the extra speed and lanes to function.
But unlike other slot sizes, the x16 slot can have different lane counts.
The most common ones are x16 (16 lanes), x8 (8 lanes), and x4 (4 lanes). This means that while the physical size of the slot is always the same, its number of lanes can vary. This is because the number of lanes is not determined by the slot itself but by the motherboard’s chipset and CPU. For example, the same PCIe x16 slot on a motherboard can have a different number of lanes with a different CPU.
Related Article: Does It Matter Which PCI-e x16 Slot I Use?
The PCIe x8 Slot
The PCIe x8 slot is not such a standard size, and most motherboards don’t have one. It is way more common to see PCIe x16 slots with eight lanes than PCIe x8 slots.
The PCIe x8 slot is smaller than the x16 slot and has eight lanes. It is mainly used for low-end graphics cards or devices that don’t need that many lanes.
The PCIe x4 Slot
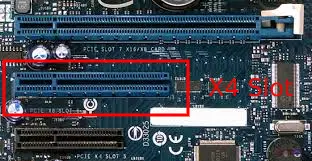
The PCIe x4 slot is very common, and almost all ATX motherboards have at least one. It is smaller than the x8 and x16 slots and has four lanes.
It became famous because it has the exact number of lanes that an M.2 SSD needs.
The PCIe x4 slot can be used for high-bandwidth network cards and M.2 SSD adapters.
The PCIe x1 Slot
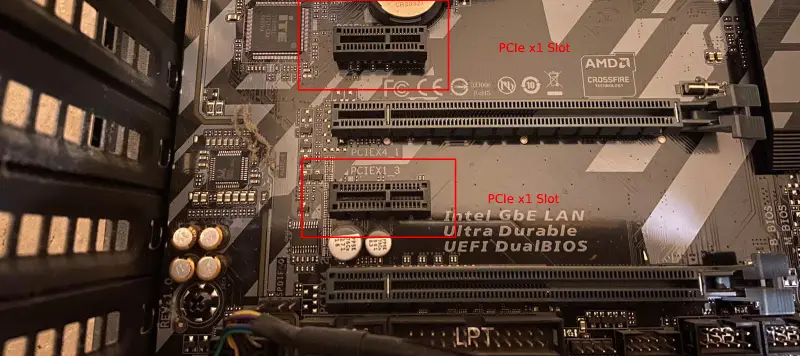
The final and smallest slot size is the PCIe x1 slot. It has only one lane and is mainly used for low-bandwidth devices such as sound cards, wifi cards, and USB 3.0 expansion cards.
You will find PCIe x1 slots in all motherboard form factors, and they are usually very easy to spot because of their small size.
Are PCIe Slots Cross Compatible?
Yes, PCIe slots are cross-compatible, but there are some things to keep in mind.
Generation Compatibility
The first thing to take into account is that PCI express slots are compatible among different generations.
For example, a PCIe 4.0 device will work in a PCIe 3.0 slot, but it will only operate at the speed of the PCIe 3.0 slot (i.e., 8 GT/s). The same is true for a PCIe 3.0 device in a PCIe 2.0 slot; it will work but at the slower PCIe 2.0 speed (i.e., 5 GT/s).
Size Compatibility
The second thing to take into account is that PCI express slots are compatible with smaller PCIe card sizes.
For example, a PCIe x1 card will work in any size PCIe slot (i.e., x1, x4, x8, x16). The only caveat is that the card will operate at its native PCIe speed; it will not be able to take advantage of the extra lanes provided by the larger slot.
On the other hand, a PCIe x16 card will only work in a PCIe x16. A PCIe x16 card can’t be placed in a PCIe x8 slot simply because it won’t fit.
I think an example will help clear this up.
Let’s say you have a PCIe 4.0 x16 graphics card and want to install it on your motherboard, but your motherboard has only one PCIe 3.0 x16 slot available; what will happen?
The card will work, but it will be limited to the speed of the PCIe 3.0 slot (i.e., 8 GT/s). So, even though the card is PCIe 4.0 capable, it will not be able to take advantage of the extra speed because the slot is slower.
The same is true if you have a PCIe 3.0 card and want to install it in a PCIe 2.0 slot; the card will work, but it will be limited to the speed of the PCIe 2.0 slot (i.e., 5 GT/s).
The takeaway is that before buying a motherboard, you should plan on what PCIe devices you want to install and ensure that the motherboard will have the correct number, generation, and size of PCIe slots.
PCIe slots and motherboard form factors
Different form factors use different numbers of PCIe slots. For example, an ATX motherboard will have more PCI express slots than an mATX or ITX motherboard.
The number and size of the slots also vary depending on the chipset used. A high-end chipset will usually have more PCIe lanes and thus more PCIe slots.
PCIe slots configuration and modes
There are so many factors involved in PCIe slots that it is pretty tricky to clearly understand how many and what generation /size of PCI express slots your motherboard has, even after looking at the specs.
This is why I am going to look at Gigabyte’s X570 Aorus Master specs and see how many PCI express slots it has and what configuration they are in.

As you can see, it has two PCIe x16 slots powered by the CPU; one PCIe x16 and one PCIe x1 slot powered by the chipset.
Let’s start with the two CPU-powered PCIe x16 slots.
If you have a Ryzen 5000 3rd generation CPU, you can use both slots in PCIe 4.0 mode at x16 and x8 speeds.
However, if you have a 2nd generation Ryzen 4000 CPU or a 3rd generation G-series, both slots will be limited to PCIe 3.0 mode.
Finally, for all other CPUs, only the top slot will work in PCIe 3.0 mode x8, and the second slot will be inactive.
Now let’s take a look at the chipset-powered PCIe slots.
The chipset-powered PCIe x16 (x4) slot will be either 4.0 or 3.0, depending on how many lanes you will be using from the CPU.
Finally, the PCIe x1 slot will also be either 3.0 or 4.0, depending on the number of CPU lanes you use.
As you can see, it is not that easy to understand all the different PCIe slot configurations.
Now that we have discussed the PCIe configurations, let’s look at the different modes.
PCIe Modes
The term PCIe modes is used to describe the different number of lanes that the PCIe device can use, depending on the number of occupied PCI express slots. It is something relevant only to the x16 slots, and the modes could be x16/x0/x0, x8/x0/x8, or x8/x4/x4.
The first number always refers to the primary slot that the graphics card is plugged into (i.e., slot 1), the second is for the second slot (i.e., slot 2), and the last is for the third slot.
x16/x0/x0
This means that if you occupy only the primary PCIe x16 slot with a graphics card, it will be able to use all 16 lanes.
x8/x8/x0
This means that if you occupy the primary PCIe x16 slot with a graphics card and the second PCIe x16 slot with another one, they will have eight lanes each. This happens because PCIe slots share the lanes. The CPU has a standard number of lanes for all three PCIe x16 slots that pass through the first slot. So if you only use the first slot, all the lanes go to it.
But as soon as you use the second slot, the number of lanes is halved.
x8/x4/x4
This means that if you occupy all three PCIe x16 slots with graphics cards, the first will be able to use eight lanes, and the second and third will use four.
The history of PCIe slots
Now that we have covered the basics of PCI express slots, let’s take a brief look at the history of this technology.
The first PCIe slot was introduced in 2004 by Intel.
The PCIe 2.0 standard was released in 2007 and doubled the bandwidth of the PCIe 1.0 standard. The first chipset to feature PCIe 2.0 slots was Intel’s X38.
The next generation of PCIe, version 3.0, was announced in 2007. However, it was not until 2010 that the first motherboard featuring PCIe 3.0 slots was released.
The next version of PCIe, version 4.0, was released in 2017 after being prematurely announced in 2011.
Finally, the latest version of PCIe, version 5.0, was released in 2021, and the Z690 chipset was the first to support it.
Related Article: How To Check If PCIe Slot Is Working?
PCIe FAQ
How Many PCIe Slots Do I Need?
The number of PCIe slots you need depends on the number of devices you want to connect to your PC. But generally, you need at least two to three slots to connect multiple devices, such as a graphics card, an SSD, or a wifi Card.
How Do I Know If My Computer Has A PCIe Slot?
The easiest way to check if your computer has a PCIe slot is to open the case and look. Alternatively, you can check the specifications of your motherboard or look in the manual.
What Is An SSD PCIe?
An SSD PCIe is a Solid State Drive that uses the PCIe interface. The speed is the main advantage of an SSD PCIe over a regular SSD because an SSD PCIe can offer much higher transfer speeds than a regular SSD.
What Is The Difference Between SATA And PCIe?
SATA and PCIe are two different types of interfaces that are used to connect storage devices to your computer.
SATA is the older interface, while PCIe is the newer and faster interface, and the main difference between SATA and PCIe is the speed.
PCIe is much faster than SATA, with a theoretical maximum speed of 63 GB/s compared to SATA’s 6 GB/s.
Related Article: SATA Port
Conclusion
Congratulations for making it to the end of this post! This was a long post, but I hope you found it informative.
We covered the differences between PCIe slot generation lanes and versions. We also talked about the different modes and speeds of PCI express slots.
I hope I have helped you understand the basics of PCIe slots and how they work.





