Deciding on whether you should upgrade your motherboard or not is not an easy choice. This is because most of the time, when you upgrade your motherboard, you will also have to upgrade other parts too because they won’t be compatible with the upgraded motherboard.
To be honest with you, most of the time, you don’t need to upgrade your motherboard. Motherboards not only have a long lifespan but also don’t affect that much your computer’s performance (like other computer parts do).
So if you want to know more about when it really makes sense to upgrade your motherboard, keep reading.
So, When Should I upgrade my motherboard?
1) Your motherboard is dead
The first and most obvious reason you might want to upgrade your motherboard is if it has stopped working. Of course, you can always try to fix it, but if it is an old model and stops working, it might be better just to upgrade it (keep in mind that if your motherboard is old and you upgrade it, you will probably have to upgrade other parts too because they won’t be compatible with the new motherboard).
And many of you would be wondering how to know when your motherboard has gone bad or is about to die. I won’t get into much detail here, but you can usually spot a dying motherboard by looking for the following signs:
- The computer doesn’t turn on
- You get the blue screen of death
- You get crashes and errors
If you want to know more about these signs and other symptoms of a dying motherboard, you can check out my guide: How To Tell If Your Motherboard Is Bad
2) When a slot or port on the motherboard is damaged
You don’t need to wait for the entire motherboard to die to upgrade it. If a certain slot or port on the motherboard gets damaged and stops working, it is a good opportunity to upgrade it. The slot that, more often than not, gets damaged is the PCI Express x16 slot. This is the slot where you plug your graphics card and is the one that gets damaged most of the time because it is exposed to all the heat coming out of your GPU.
However, other ports or slots that are considered less important can also get damaged, especially if you are using them a lot. So, If there are certain ports or slots on your motherboard that are important for you and don’t work, you should consider upgrading your motherboard.
3) You want to upgrade your system

As you already know, a computer system has many components that are connected to the motherboard, and if you want to upgrade even one of them, you might have to upgrade the motherboard too.
So, let’s see in more detail the most common upgradable parts and how they can affect your motherboard choice.
a) CPU upgrade
The most common internal component people upgrade is the CPU. The CPU is the heart of your computer, and it greatly affects its performance. But unfortunately, most of the time, when you upgrade your CPU, you will also have to upgrade your motherboard, as not all CPUs are compatible with all motherboards. To learn when you can keep your old motherboard if you upgrade your CPU and when you have to upgrade your motherboard too, check my article: Upgrade CPU Without Changing Motherboard?
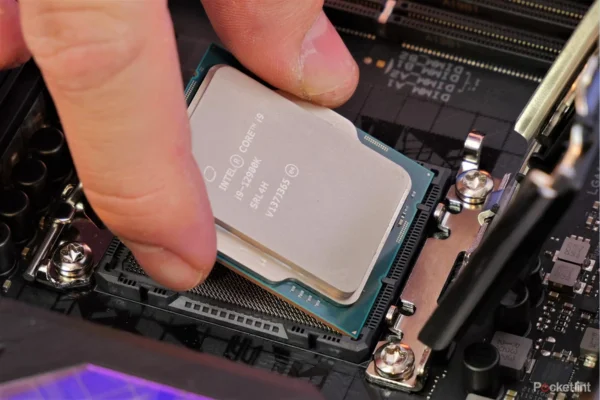

But to give you a quick overview, let me say that two major factors affect if a CPU is compatible with a motherboard:
- The Socket type: Every motherboard has one CPU socket where you should plug your CPU, but not all sockets are compatible with all CPUs, and if they are not compatible, the CPU won’t physically fit. To see if your new CPU is compatible with your old motherboard or if you have to upgrade it, you have to check both the specs of the new CPU and the old motherboard and see if they match.
- Chipset: While most people know about socket compatibility and pay attention to it, they don’t pay that much attention to the chipset. The chipset is the motherboard’s main chip and is responsible for connecting all the components on your motherboard (CPU, RAM, slots, ports). It also determines the BIOS version of your motherboard, and if the BIOS version is not compatible with the CPU, you will have to upgrade it, which can result in all kinds of problems.
| Socket Name | CPU Support | Year of Introduction |
|---|---|---|
| LGA 1700 | 12th and 13th Gen. Desktop Intel CPUs | 2021 |
| LGA 1200 | 10th and 11th Gen. Desktop Intel CPUs | 2020 |
| AM4 | All Mainstream Desktop AMD Ryzen CPUs | 2017 |
| LGA 1151 | 7th, 8th, and 9th Gen. Desktop Intel CPUs | 2017 |
b) You want to upgrade your GPU or add a second one
Another very common upgrade reason, especially amongst gamers, is when they want to upgrade their GPU or plug a second one and need to get a motherboard that supports dual GPU usage.
But why change your motherboard when you get a new GPU?
As I already mentioned earlier, the slot used for GPUs is the PCIe x16 slot. But not all PCIe x16 slots are the same. The main difference between PCIe x16 slots is their generation. PCI Express has many different generations, and the newer generation, the faster the data transfer speed. At this point, I would like to mention that PCIe slots are cross-compatible, meaning you could use a new (PCIe 4.0 or PCI 5.0) GPU on a motherboard that supports PCIe 3.0, but the data transfer speed will be capped to the lower generation.
Other than the generation, there is another major difference between PCIe x16 slots: The number of lanes. The number of lanes is a very complex topic, and if you want to know more about it, I strongly advise reading this and this article, but to give you a quick preview, a PCIe x16 slot can have anywhere from 1 to 16 lanes. And like the PCIe generation, the number of lanes directly affects the data transfer speed.
To understand how much these two factors affect the data transfer speed, check this table:
| Generation | x16 GB/s | x8 GB/s | x4 GB/s | x2 GB/s | x1 GB/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 | 63.015 | 31.508 | 15.754 | 7.877 | 3.938 |
| 4.0 | 31.508 | 15.754 | 7.877 | 3.938 | 1.969 |
| 3.0 | 15.754 | 7.877 | 3.938 | 1.969 | 0.985 |
| 2.0 | 8.000 | 4.000 | 2.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 |
| 1.0 | 4.000 | 2.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 0.250 |
So as you can understand, a new motherboard upgrade is essential when upgrading your graphics card.
c) RAM upgrade
RAM upgrade is another very common upgrade and one that might force you to upgrade your motherboard.
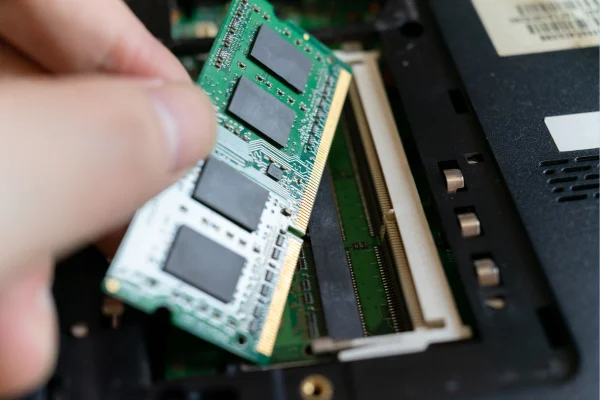

But when is it necessary to upgrade your motherboard when you upgrade your RAM?
If you want to listen to the long answer, you can check my article about RAM and motherboard compatibility, but if you don’t care that much about the geeky details and want the short version, let me briefly list the important factors when deciding if you have to upgrade your motherboard when adding a faster RAM:
- RAM type: Just like PCI Express, there are different generations of RAM, and the newer generation, the faster the data transfer speed. The latest and fastest RAM generation is DDR5 which is still relatively new, with the most common being DDR4. But the biggest difference between RAM and PCIe is that RAM is not cross-compatible. This means that a DDR4 RAM stick won’t physically fit into a DDR 5 slot, and you will have to upgrade your motherboard if you want a newer generation RAM.
- RAM frequency: Another factor that affects the compatibility of your RAM with your motherboard is its frequency. The frequency of RAM is a fancy word to describe its speed. Motherboards support certain RAM frequency ranges, and if the RAM frequency of your new RAM stick is higher than the supported range, you will have to upgrade your computer’s motherboard (unlike RAM generation, the frequency is cross-compatible, meaning you can use higher frequency new RAM modules on a motherboard that supports lower frequencies, but you will be capped to the range of your motherboard).
- The number of RAM slots: This is straightforward but many times overlooked. If you want to upgrade your RAM, make sure there are free RAM slots on your motherboard, or you will have to upgrade.
- RAM Capacity: Finally, the RAM capacity of your motherboard has also to be checked. The RAM capacity is the maximum amount of RAM that your motherboard can support and is measured in GBs. If you want to upgrade your RAM, make sure it is the same or lower than the maximum motherboard capacity, or you’ll have to upgrade.
d) You want a faster storage drive
A major factor that affects your computer system’s speed is its storage drive. Storage drives store everything from the operating system to your data, and the faster they are, the faster your system will be.
But when is it necessary to upgrade your motherboard when upgrading your storage drive?
It all depends on the technology and the type of storage drive.
The most used technologies for SSDs are SATA and NVMe. SATA drives use the SATA protocol, and there are different versions of it: SATA I, II, and III. The difference between them is the data transfer rate, meaning that a SATA I SSD would be much slower than a SATA III SSD.
NVMe drives, on the other hand, use the PCIe protocol and have superior transfer rates than SATA drives.
And if you are wondering why you should care about all that, it is because if you want to go from a SATA SSD to an NVMe SSD and your motherboard doesn’t have an NVMe PCIe slot (m.2), you will have to upgrade your motherboard to be able to use that more advanced drive (There are some workarounds though, like using an NVMe m.2 to PCIe adapter, but you get my point).
e) You want more networking and connectivity options
While this is the less important reason to do a motherboard upgrade, it is something worth mentioning.
Your motherboard is responsible for the networking features and connectivity options of your system, such as the LAN capabilities, WiFi adapter, Bluetooth connection, the number and type of USB ports, audio jacks, etc.
The truth is that most of these features can be upgraded by adding an expansion card to your motherboard, but if your motherboard is very old and you are a content creator that uses many peripherals, it is probably a better idea to upgrade your motherboard.
4) You want to overclock
I left that for the end because if you decide to overclock your system (CPU, RAM, etc.) you should not be reading this article as you are probably a more experienced user.
Overclocking is the process of increasing the performance of computer hardware by modifying its default settings to push its performance further.
The most common hardware that most users overclock is the CPU, and the motherboard plays a major role in whether or not you can overclock your CPU and if the overclock is stable.
There are two main reasons why the motherboard plays a vital role in overclocking:
- The first one is that it should be able to provide your CPU with enough power. If the power is insufficient, you will have performance problems and random shutdowns. The motherboard part responsible for providing power to the CPU is the VRM. VRM stands for Voltage Regulator Module, and is responsible for converting the power from your PSU to the voltage that your CPU needs. So, if you plan to overclock your CPU, always make sure to buy a motherboard with powerful VRMs.
- The second one is that because of the huge power delivery, motherboards’ VRMs get really hot when overclocking, and a good quality heatsink is necessary to dissipate all the heat.
I guess you can now understand why if you plan to overclock your system, you can’t use your current motherboard, and you need a new one designed for overclocking.
Conclusion
By now, you should be able to know when to upgrade your computer motherboard and why.
If you decide to upgrade your motherboard and need help finding the right one for you, don’t hesitate to leave a comment below, and I will do my best to help you out!
Thank you for reading this article, and I wish you the best of luck with upgrading your motherboard!