If you’ve noticed your GPU running hot and are wondering why, the answer might lie in the GPU’s hotspot temperature. Unlike the average temperature you usually monitor, the hotspot temperature represents the single hottest point on the graphics card—and it can be significantly higher.
High hotspot temperatures can lead to performance drops, overheating, or even long-term damage if ignored. Read on to know what GPU hotspot temperature is, what a safe range looks like, and how you can manage it to keep your system running smoothly.
What is a GPU Hotspot?
A GPU hotspot refers to the single hottest point on the GPU die, which is often significantly higher than the average temperature reported by monitoring software.

The difference between the average GPU temperature and the hotspot can be quite significant, often ranging between 10°C to 15°C higher. For instance, if your average GPU temperature is 75°C, the hotspot might be pushing 85°C to 90°C or higher.
Both NVIDIA and AMD have implemented more advanced thermal monitoring in their newer GPUs. For example, AMD’s RDNA 2 GPUs have a feature called “Junction Temperature,” which specifically measures the hotspot. In their official data, AMD has stated that a maximum junction (hotspot) temperature of around 110°C is considered acceptable for their GPUs. However, exceeding this limit for prolonged periods can lead to performance degradation.
Software like HWMonitor, GPU-Z, and MSI Afterburner allow users to monitor GPU hotspot temperatures specifically.
Safe Operating Ranges for GPU Hotspot Temperatures
While modern GPUs are designed to handle higher temperatures, it’s best to maintain temperatures in the lower end of the safe range for the best results.
Optimal Range: Below 70°C
For optimal performance, GPU hotspot temperatures should ideally remain below 70°C. At this temperature, the GPU operates efficiently, allowing for maximum performance without the risk of overheating. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning dust from fans and ensuring proper airflow within the case, can help maintain these temperatures. Keeping the GPU in this range not only enhances performance but also extends its lifespan.
Safe Range: 70°C to 85°C
Temperatures between 70°C and 85°C are generally considered safe for most GPUs. While this range is slightly higher than optimal, it still allows for effective performance without significant risk of damage. During heavy workloads, such as gaming or rendering, it’s common for GPUs to reach these temperatures. To maintain this range, ensure adequate case ventilation and consider using additional cooling solutions if necessary.
High but Acceptable Range: 85°C to 95°C
Hotspot temperatures in the range of 85°C to 95°C are on the higher side but can still be acceptable for modern GPUs, especially during intense usage. However, prolonged exposure to these temperatures can lead to thermal throttling, where the GPU reduces its performance to manage heat. If your GPU frequently operates in this range, it’s advisable to enhance cooling measures, such as improving airflow or using aftermarket cooling solutions.
Danger Zone: Above 95°C
Temperatures exceeding 95°C are concerning and indicate a risk of thermal throttling and potential damage to the GPU. At this level, the GPU may automatically reduce its clock speeds to prevent overheating, leading to noticeable performance drops. Sustained temperatures above this threshold can cause long-term damage to the hardware. If your GPU consistently reaches temperatures in this range, it’s crucial to take immediate action—such as improving airflow, reapplying thermal paste, or upgrading your cooling system—to prevent serious damage.
Causes of GPU Hotspots

GPU hotspots can be a significant concern for anyone using a graphics card, especially during demanding tasks. Here are some of the primary causes of these hotspots:
Heavy Workload
When your GPU is pushed to its limits—such as during high-end gaming, video rendering, or complex graphical tasks—it generates a considerable amount of heat. This intense activity can lead to localized overheating, resulting in hotspots on the GPU.
Poor Ventilation

A well-ventilated computer case is crucial for maintaining optimal temperatures. If the airflow is restricted—either due to a cluttered case filled with dust or inadequate fan placement—the GPU may struggle to cool itself effectively. This lack of airflow can cause heat to build up, leading to hotspots.
Overclocking

Some users attempt to enhance their GPU’s performance by overclocking, which means running the graphics card at higher speeds than it was designed for. While this can boost performance, it also increases heat output, potentially overwhelming the GPU’s cooling system and creating hotspots.
Old or Faulty Fans

The fans on a GPU play a vital role in dissipating heat. If these fans are old, malfunctioning, or clogged with dust, they may not provide adequate cooling. This inefficiency can contribute to higher temperatures and the formation of hotspots.
Improper Cooling System
The cooling system itself, including components like heat sinks and thermal paste, must be installed and functioning correctly. If thermal paste is old or improperly applied, or if the heat sink is not making good contact with the GPU, it can lead to inefficient heat transfer and increased hotspot temperatures.
Environmental Temperature
The ambient temperature of the room where the computer is located can also impact GPU performance. If the environment is particularly warm, it becomes more challenging for the GPU to dissipate heat effectively, which can lead to hotspots forming during operation.
Symptoms of a GPU Hotspot Issue
When dealing with GPU hotspots, recognizing the symptoms of an overheating issue is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of your graphics card. Here are some common signs that indicate you might be facing a GPU hotspot problem:
Performance Issues
One of the first symptoms you may notice is a drop in performance during gaming or graphic-intensive tasks. If your GPU is overheating, it may throttle down its performance to avoid damage. This can result in stuttering, lagging, or frame rate drops, making your gaming experience less enjoyable.
Increased Fan Noise
As the GPU heats up, the cooling system kicks into high gear to try to dissipate the excess heat. This often leads to noticeably louder fan noise as they work harder to maintain lower temperatures. If you find your GPU fans running at maximum speed frequently, it could be a sign of hotspot issues.
Crashes and Instability
In more severe cases, high hotspot temperatures can lead to system instability. You might experience unexpected crashes, freezes, or even blue screens of death (BSOD) while using your computer. These issues often arise when the GPU is unable to handle the thermal stress, forcing the system to shut down to prevent damage.
Visual Artifacts
Overheating can also manifest as visual artifacts on your screen. This could involve odd lines, flickering, or other visual issues. If you notice these anomalies while gaming or using graphics-intensive applications, it could indicate that your GPU is struggling with heat management.
Thermal Throttling
If you monitor your GPU temperatures and notice that they frequently reach high levels, you may be experiencing thermal throttling. This is when the GPU automatically reduces its clock speeds to lower its temperature, impacting overall performance. Keeping an eye on both average and hotspot temperatures can help you identify this issue.
Consistently High Hotspot Temperatures
Finally, if you have monitoring software that shows consistently high hotspot temperatures, this is a clear indicator of a problem. While average GPU temperatures might seem normal, hotspots can reveal hidden thermal issues that need to be addressed.
How to Monitor GPU Hotspot Temperature
Use Built-in Monitoring Tools
Most modern GPUs come with built-in monitoring tools that allow you to track temperatures easily.
- NVIDIA GeForce Experience: If you have an NVIDIA GPU, you can use GeForce Experience to monitor temperatures. Launch the application, go to the in-game overlay settings, and enable the performance overlay. This will display real-time GPU stats, including temperature, while you game.
- AMD Radeon Software: For AMD users, the Radeon Software provides a straightforward way to monitor GPU temperatures. Open the software, navigate to the “Performance” tab, and you’ll find real-time temperature readings along with other performance metrics.
- Windows Task Manager: In Windows 10 and 11, you can check your GPU temperature directly from Task Manager. Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc, click on the “Performance” tab, and select “GPU” from the left sidebar. The current temperature will be displayed at the bottom of the window.
Third-Party Monitoring Software
While built-in tools are convenient, third-party software often provides more detailed insights and customization options. Here are some popular options:
- MSI Afterburner: This is a widely used tool among gamers and enthusiasts. It not only monitors GPU temperatures but also allows you to adjust fan speeds and overclock your GPU. You can set custom fan curves to ensure your GPU stays cool under load.
- HWMonitor: This tool provides comprehensive monitoring of your GPU and other system components. It displays real-time temperature readings, voltages, and fan speeds, allowing you to keep an eye on your GPU’s thermal performance.
- GPU-Z: This lightweight application focuses specifically on GPU monitoring. The “Sensors” tab shows real-time temperature readings, load percentages, and more. It’s particularly useful for tracking how your GPU behaves during various workloads.
Command-Line Tools
For those who prefer a more technical approach, command-line tools can provide precise temperature readings:
NVIDIA-SMI: If you have an NVIDIA GPU, you can use the NVIDIA System Management Interface (nvidia-smi) to check temperatures. Open Command Prompt and enter this command:
nvidia-smi –query-gpu=gpu_name,temperature.gpu –format=csv
This command will return the GPU name along with its current temperature in Celsius.
How to Prevent and Fix GPU Hotspot Issues
1. Optimize Airflow
Case Configuration: Ensure that your PC case has adequate airflow. This involves positioning fans to create a positive airflow system where cool air enters from the front and hot air exits from the back and top.
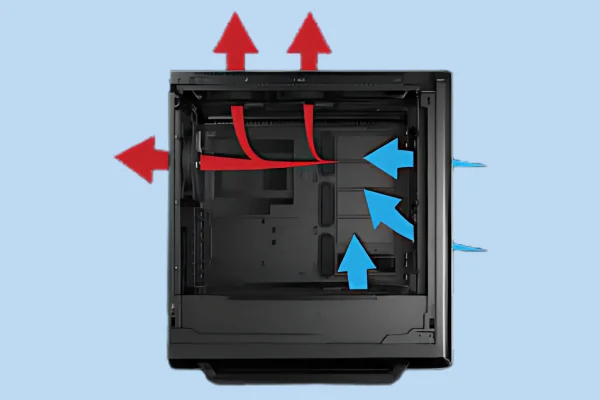
Fan Placement: Consider adding more case fans or upgrading existing ones for better airflow. Larger fans can move more air at lower RPMs, reducing noise while improving cooling efficiency.
2. Regular Cleaning
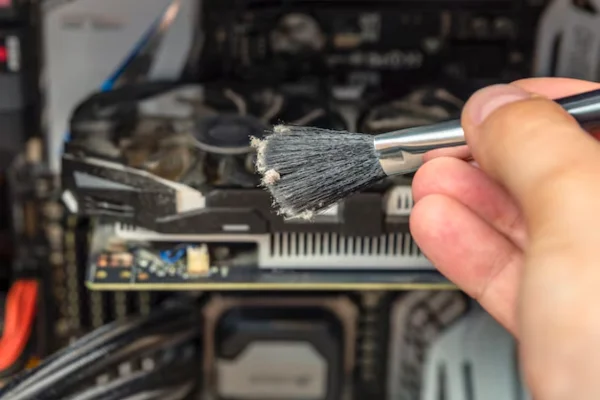

Dust accumulation can significantly hinder cooling performance. Regularly clean your GPU and the interior of your case using compressed air to remove dust from fans, heatsinks, and other components. This simple maintenance task can dramatically improve thermal performance.
3. Upgrade Cooling Solutions
Aftermarket Coolers: If your GPU is frequently overheating, consider investing in an aftermarket cooler. High-performance air coolers or liquid cooling solutions can provide superior heat dissipation compared to stock coolers.
Thermal Paste: Over time, the thermal paste between the GPU and its heatsink may wear out. Reapplying high-quality thermal paste every few years can enhance heat transfer efficiency, helping to keep temperatures down.
4. Monitor and Adjust Fan Curves
Most modern GPUs allow for fan curve customization through software like MSI Afterburner or GPU manufacturer’s software. By setting a more aggressive fan curve, you can ensure that the fans ramp up more quickly in response to rising temperatures, helping to control hotspots.
5. Undervolting and Underclocking
Reducing the voltage supplied to your GPU can decrease power consumption and heat output without significantly impacting performance. Software tools like MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X1 can help you safely undervolt and underclock your GPU.
6. Avoid Overclocking
Although overclocking can improve performance, it also causes more heat. If you’re experiencing hotspot issues, it’s best to avoid overclocking until you have a robust cooling solution in place.
7. Environmental Considerations
Room Temperature: The ambient temperature of your gaming environment can greatly affect GPU temperatures. Keep your room well-ventilated and at a cooler temperature to help manage internal system temperatures.
Cable Management: Ensure that cables do not obstruct airflow within the case. Neat and organized cables can improve circulation, allowing for better cooling around the GPU.
8. Use Monitoring Software
Regularly monitor your GPU temperatures using software like HWMonitor, GPU-Z, or MSI Afterburner. Set alerts for when temperatures exceed safe thresholds, allowing you to take action before overheating becomes a problem.
9. Identify and Address Hotspots
Use thermal imaging or infrared thermometers to identify specific hotspots on your GPU. Once identified, you can take targeted actions, such as adjusting cooling solutions or improving airflow in those areas.
Conclusion
Managing GPU hotspot temperatures is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of your graphics card.
Regular monitoring, cleaning, and upgrading cooling solutions are essential practices that can significantly enhance your GPU’s thermal management. Whether optimizing airflow, upgrading cooling systems, or adjusting fan settings, proactive measures will help ensure your GPU remains within safe temperature limits during demanding tasks.





