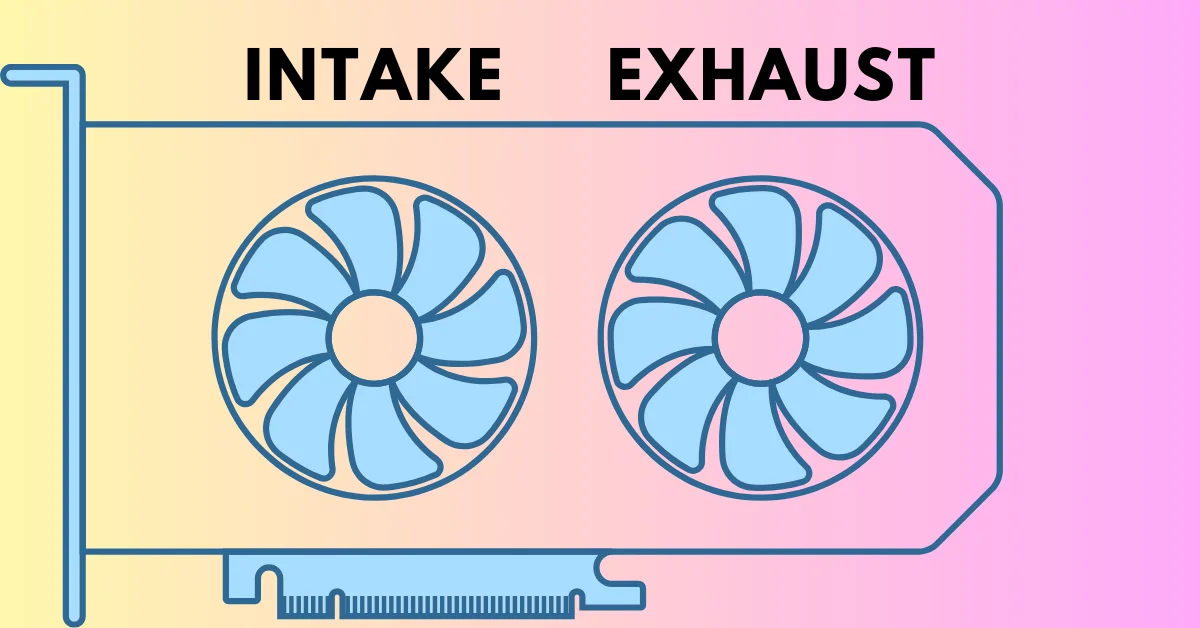
When it comes to keeping your graphics card cool, GPU fans play a crucial role. But one common question arises: Are GPU fans function as intake or exhaust fans? Some GPU fans pull cool air onto the card, while others push hot air out of the case.
Keep reading to clarify whether your GPU fans are working as intake or exhaust, helping you optimize your PC’s cooling setup.
Types of GPU Cooling Systems
GPU coolers are available in different types but two primary types are: blower-style coolers and open-air coolers. Each cooling system operates differently, affecting whether the GPU fans function as intake or exhaust.
| Cooler Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open-air coolers | Fans blow air onto heatsink | Efficient, quiet, good for ventilated cases | Disperses heat into the case |
| Blower-type coolers | Single fan expels air out | Great for small cases, directs heat outside | Louder, less efficient |
| Liquid coolers (AIO) | Closed-loop system with water block & radiator | Excellent cooling, quieter | Expensive, needs radiator space |
| Custom water cooling | User-built loop | Best performance, customizable | Expensive, complex, needs maintenance |
| Hybrid coolers | Combines air and liquid cooling | Balanced performance | Costlier, less efficient than full liquid |
| Passive coolers | Heatsinks, no fans | Silent operation | Low cooling capacity, for low-power GPUs |
Are GPU Fans Typically Intake or Exhaust?
Most GPU fans are designed to act as exhaust fans. Their primary role is to expel the hot air generated by the GPU during operation, which is essential for maintaining optimal thermal performance. By pushing hot air out of the case, these fans help prevent heat buildup around the GPU and other components.
In typical setups, GPU fans pull air across the heatsink and expel it out of the back of the card, cooling the GPU and aiding overall system airflow. This expelled hot air is then managed by the case’s exhaust fans, helping to maintain a balanced airflow throughout the system. Proper case ventilation, with a good balance of intake and exhaust fans, is key to ensuring efficient cooling and a stable computing environment.
Pros and Cons of GPU Fan Configurations
Exhaust Fan Configuration
Advantages:
- Efficient heat dissipation
- Space-saving design
- Cost-effectiveness
Disadvantages:
- Potential for limited airflow compared to dedicated fans
- Noise levels under load
Intake Fan Configuration
Advantages:
- Direct supply of cooler air to the GPU
- Positive air pressure benefits
Disadvantages:
- Risk of heat buildup if not balanced with exhaust fans
- Increased dust accumulation
Impact on Case Airflow
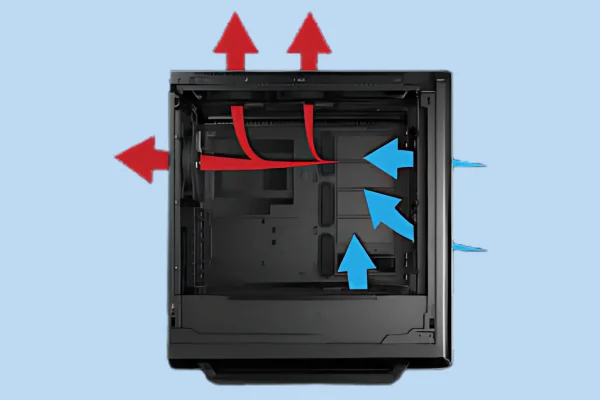
The way GPU fans manage airflow has a significant impact on the overall thermal dynamics of your PC case. In blower-style GPUs, the hot air is directly exhausted out of the case, which helps isolate the GPU’s heat from the rest of the system. This design is especially useful in compact cases or multi-GPU setups, as it prevents the heat from lingering inside the case, reducing the overall temperature of other components.
In contrast, open-air GPU coolers, which use intake fans, disperse the hot air back into the case. While they cool the GPU efficiently, they rely on the case’s exhaust fans to handle the additional heat inside. For this reason, a well-ventilated case with sufficient exhaust fans is crucial for open-air coolers to prevent heat buildup.
A well-balanced system typically follows the 2:1 or 3:2 rule, where you have more intake fans than exhaust. This slight positive pressure ensures that cool air is being drawn into the case at a higher rate, which helps open-air GPU coolers perform better. On the other hand, blower-style GPUs thrive in cases with strong exhaust setups, as their cooling method already handles hot air efficiently. Understanding how GPU fans affect case airflow helps optimize cooling for different builds, whether you’re using blower-style or open-air cards.
Conclusion
While GPU fans can be categorized as either intake or exhaust, it is clear that most GPU fans are typically designed to function as exhaust fans. This configuration allows them to efficiently expel the hot air generated during operation, thereby enhancing the overall cooling performance of the system.